Precision, speed, and motion stability define the performance limits of modern automation systems. As industrial applications demand smoother trajectories, higher positioning accuracy, and shorter cycle times, conventional rotary-driven mechanisms increasingly struggle with mechanical losses and system complexity. Linear Synchronous Motors address these challenges by delivering direct, perfectly synchronized linear motion through advanced electromagnetic control. This technology enables a level of efficiency, responsiveness, and precision that reshapes how high-performance motion systems are designed and deployed across industrial environments.
What Are Linear Synchronous Motors?
Linear Synchronous Motors (LSMs) are a class of direct-drive linear motors designed to generate precise linear motion through electromagnetic synchronization. Unlike conventional motion systems that rely on rotary motors combined with mechanical transmission elements such as ball screws, belts, or gearboxes, LSMs produce linear movement directly, eliminating intermediate mechanical components and their associated losses.
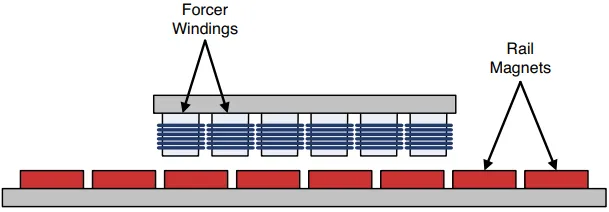
At their core, Linear Synchronous Motors operate on the same physical principles as rotary synchronous motors. The key difference lies in geometry: instead of converting rotational motion into linear displacement, LSMs “unroll” the motor structure to create motion along a straight path. This direct linear architecture allows LSMs to achieve exceptionally high positioning accuracy, smooth motion profiles, and dynamic response that are difficult to match with traditional drive systems.
From a system-level perspective, Linear Synchronous Motors are widely recognized as a high-end motion solution for applications where speed, precision, and long-term reliability are critical. They are commonly used in environments that demand continuous, repeatable performance under tight tolerances, such as semiconductor manufacturing, precision automation, and advanced industrial machinery.
A Linear Synchronous Motor is a linear motor in which the moving part travels in exact synchronism with a traveling electromagnetic field generated by the motor windings. This synchronous behavior means there is no relative slip between the magnetic field and the mover, enabling highly accurate control of position, velocity, and acceleration.
Most Linear Synchronous Motors are based on permanent magnet technology, often referred to as Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors (PMSMs). In these systems, permanent magnets mounted on the secondary side interact with a precisely controlled alternating current supplied to the primary windings. The resulting electromagnetic force drives the mover along a linear axis with deterministic and repeatable motion characteristics.
Because motion is fully synchronized with the control signal, LSMs are particularly well-suited for servo-controlled applications that require complex motion profiles, rapid start-stop cycles, and smooth interpolation without mechanical backlash.
Working Principle of Linear Synchronous Motors
Linear Synchronous Motors operate based on the principle of electromagnetic synchronization between a traveling magnetic field and a moving magnetic structure. Instead of generating rotational torque, the motor produces a continuous linear force that drives motion along a straight path with precise control over position, velocity, and acceleration.
At a fundamental level, the motor “unrolls” the structure of a conventional synchronous motor, transforming rotary motion into direct linear displacement. This design allows electromagnetic forces to act directly on the load, eliminating the need for mechanical transmission components and enabling highly efficient motion generation.
Generation of a Traveling Magnetic Field
The working process begins in the primary side of the motor, where three-phase alternating current is supplied to the stator windings by a servo drive. These currents are precisely controlled in amplitude, frequency, and phase, creating a traveling electromagnetic field that moves linearly along the motor axis.
The speed of this traveling magnetic field is directly proportional to the frequency of the supplied current. By adjusting this frequency, the control system determines the velocity of the motor with high accuracy. Because the magnetic field itself defines the motion reference, the system can achieve smooth acceleration and deceleration without mechanical delays or backlash.
Synchronous Interaction with the Mover
On the secondary side, permanent magnets are arranged in a specific magnetic pattern to interact with the traveling field generated by the primary. The magnetic poles of the mover continuously align with the moving electromagnetic field, resulting in a synchronized linear force.
This synchronous behavior means that the mover follows the traveling field without slip. Unlike induction-based linear motors, where relative motion between the field and the conductor is required to generate force, Linear Synchronous Motors maintain exact synchronization at all times. This characteristic is essential for applications requiring deterministic motion and high positioning accuracy.
Role of Permanent Magnets and Force Production
Permanent magnets in Linear Synchronous Motors provide a constant magnetic flux, which significantly improves force density and efficiency. As the traveling electromagnetic field interacts with this magnetic flux, a Lorentz force is generated, driving the mover along the linear axis.
Because the magnetic field strength of the permanent magnets remains stable, the motor can deliver consistent force across a wide operating range. This stability contributes to smooth motion profiles, reduced torque ripple, and excellent repeatability, even during rapid start-stop cycles or complex motion trajectories.
Closed-Loop Control and Motion Synchronization
Precise motion control in Linear Synchronous Motors is achieved through closed-loop servo control. High-resolution linear encoders or position sensors continuously measure the exact position of the mover and feed this information back to the motion controller.
Using advanced control algorithms, the servo drive dynamically adjusts current magnitude and phase to maintain perfect synchronization between the traveling magnetic field and the mover. This real-time correction ensures accurate positioning, stable velocity, and optimal force output under varying load conditions.
Why No Slip Matters in Linear Motion Control
One of the defining characteristics of Linear Synchronous Motors is the absence of slip between the magnetic field and the mover. Since motion is directly tied to the control signal, the motor responds immediately to command changes, enabling highly predictable and repeatable motion.
This slip-free operation not only enhances positioning accuracy but also reduces energy losses and heat generation. As a result, Linear Synchronous Motors are especially suitable for high-performance automation systems where thermal stability and long-term reliability are critical.
By combining a traveling electromagnetic field, permanent magnet interaction, and closed-loop servo control, Linear Synchronous Motors translate electromagnetic theory into practical industrial motion. The result is a direct-drive system capable of delivering high speed, high precision, and smooth linear motion without the limitations of mechanical transmission.
This working principle forms the foundation for the superior performance characteristics and broad industrial adoption of Linear Synchronous Motors.
Key Advantages of Linear Synchronous Motors
Linear Synchronous Motors are engineered to overcome the mechanical and performance limitations of conventional motion systems. By delivering direct, synchronized linear motion, they unlock a set of advantages that directly translate into higher productivity, improved accuracy, and long-term system reliability.
- Direct-drive linear motion without mechanical transmission: Linear Synchronous Motors generate force directly on the moving load, eliminating ball screws, belts, and gearboxes. This direct-drive architecture removes mechanical backlash, reduces inertia, and ensures that motion commands are executed with immediate and predictable response.
- Exceptional positioning accuracy and repeatability: Because motion is fully synchronized with the electromagnetic field, Linear Synchronous Motors achieve extremely high positioning precision, often at sub-micron levels. This makes them ideal for applications requiring tight tolerances, smooth interpolation, and consistent repeatability over long operating cycles.
- High speed and dynamic acceleration: The absence of mechanical constraints allows Linear Synchronous Motors to reach very high linear speeds and accelerations. Rapid start-stop capability and smooth motion profiles significantly reduce cycle times in high-throughput automation systems.
- Superior energy efficiency and force density: With no rotor losses and minimal energy dissipation, Linear Synchronous Motors deliver higher efficiency compared to induction-based linear drives. The use of permanent magnets enables strong and stable force output while reducing overall power consumption.
- Low heat generation and improved thermal stability: Reduced electrical and mechanical losses lead to lower heat generation in the motion system. This thermal stability improves positioning accuracy, protects sensitive components, and simplifies thermal management in precision environments.
- Minimal maintenance and long service life: Frictionless, contactless motion dramatically reduces wear and tear. Without mechanical transmission elements to degrade over time, Linear Synchronous Motors offer longer operational life and lower maintenance costs.
- Compact system design and greater machine flexibility: By eliminating bulky mechanical components, Linear Synchronous Motors enable more compact and flexible machine layouts. This design freedom allows engineers to optimize space utilization and integrate motion systems more easily into complex automation architectures.
Together, these advantages position Linear Synchronous Motors as a strategic choice for high-performance motion systems. Their ability to combine speed, precision, efficiency, and reliability makes them a foundational technology for advanced automation and next-generation industrial applications.
Applications of Linear Synchronous Motors
Linear Synchronous Motors are widely adopted in industries where motion performance directly impacts product quality, throughput, and system reliability. Their ability to deliver fast, precise, and fully synchronized linear motion makes them a preferred solution across a broad range of high-performance applications.
- Semiconductor manufacturing equipment: Linear Synchronous Motors are extensively used in wafer handling, lithography stages, and inspection systems, where ultra-high positioning accuracy and smooth motion are critical. Their low heat generation and vibration-free operation help maintain process stability in cleanroom environments.
- High-speed automation and assembly systems: In automated production lines, Linear Synchronous Motors enable rapid acceleration, precise positioning, and repeatable motion profiles. These characteristics significantly reduce cycle times while maintaining consistent product quality across high-volume manufacturing processes.
- Precision machine tools and CNC systems: For applications requiring accurate contouring and smooth interpolation, Linear Synchronous Motors provide direct-drive motion without backlash. This results in superior surface finish, improved machining accuracy, and reduced mechanical complexity.
- Robotics and pick-and-place applications: Linear Synchronous Motors support fast, precise, and synchronized motion in robotic axes and pick-and-place systems. Their responsiveness and repeatability improve throughput while ensuring accurate placement in high-speed material handling tasks.
- Automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS): In logistics and warehousing environments, Linear Synchronous Motors deliver reliable, high-speed linear motion for shuttles and transfer units. Their efficiency and low maintenance requirements contribute to long-term operational stability in continuous-duty systems.
- Medical and laboratory automation: Applications such as diagnostic equipment, sample handling, and imaging systems benefit from the smooth, quiet, and precise motion provided by Linear Synchronous Motors. The absence of mechanical wear supports consistent performance and high reliability in sensitive environments.
- Electronics manufacturing and inspection: In PCB assembly, testing, and inspection systems, Linear Synchronous Motors ensure precise alignment and controlled motion. This precision is essential for maintaining quality standards in increasingly miniaturized electronic components.
- Transportation and advanced motion platforms: Linear Synchronous Motors are also applied in specialized transportation systems and experimental motion platforms, where synchronized linear force and high dynamic performance are required for smooth and controlled movement.
Across these applications, Linear Synchronous Motors consistently demonstrate their value by enabling higher precision, faster operation, and improved system reliability. Their versatility and performance make them a foundational motion technology for industries pushing the limits of speed, accuracy, and automation.
Linear Synchronous Motors vs Other Linear Motor Technologies
Linear motion can be achieved through several motor technologies, each with distinct performance characteristics and application boundaries. Among these options, Linear Synchronous Motors stand out for their ability to deliver fully synchronized, high-precision motion, particularly in demanding industrial environments.
Compared to Linear Induction Motors, Linear Synchronous Motors operate without slip between the traveling magnetic field and the mover. This fundamental difference results in significantly higher positioning accuracy, better efficiency, and more predictable motion behavior. While Linear Induction Motors are often favored for simpler, cost-sensitive applications or long transport distances, they typically generate more heat and offer lower force density, making them less suitable for precision-driven systems.
When evaluated against iron-core and ironless linear motors, Linear Synchronous Motors provide a balanced combination of force output and smoothness. Iron-core designs deliver high thrust but can introduce cogging forces, while ironless configurations excel in smooth motion at the expense of lower force density. Linear Synchronous Motors, especially permanent magnet-based designs, achieve strong thrust with stable motion control, making them adaptable to a wide range of industrial requirements.
In comparison with mechanical linear drive systems such as ball screws, rack-and-pinion, or belt-driven mechanisms, Linear Synchronous Motors eliminate mechanical contact and transmission losses entirely. Mechanical systems inherently suffer from backlash, wear, and maintenance requirements that limit long-term accuracy and dynamic performance. Linear Synchronous Motors overcome these constraints by providing direct-drive motion, reducing system inertia and improving responsiveness.
From a control perspective, Linear Synchronous Motors integrate seamlessly with advanced servo drives and motion controllers. Their synchronous nature allows precise coordination across multiple axes, supporting complex motion profiles that are difficult to achieve with induction-based or mechanically driven systems.
Conclusion
Linear Synchronous Motors represent a fundamental shift in how high-performance motion systems are designed and controlled. By combining direct-drive architecture, synchronous electromagnetic control, and exceptional precision, they eliminate the limitations of mechanical transmission and unlock new levels of speed, efficiency, and reliability. As industrial applications continue to demand tighter tolerances and higher productivity, Linear Synchronous Motors stand out as a future-ready motion solution, empowering manufacturers and system integrators to build smarter, faster, and more precise automation systems.

