Precision, power, and control, that’s what sets high torque servo motors apart in the world of motion systems. These motors are trusted in high-demand environments where every movement must be accurate and efficient.
While hall sensor motors also offer a cost-effective solution for basic torque needs, they operate on a fundamentally different level of performance. If you’re evaluating which motor technology best suits your application, this comparison will walk you through the strengths, weaknesses, and real-world use cases of both, while highlighting why high torque servo motors remain the preferred choice for advanced automation systems.
What Are High Torque Servo Motors?
High torque servo motors are specialized motors designed to deliver precise control of angular position, velocity, and acceleration, while also generating significantly high torque output. Unlike standard motors, servo motors are part of a closed-loop control system, which means they constantly receive feedback from sensors (typically encoders) to adjust their position and speed in real time.
At the core of a high torque servo motor is a highly efficient brushless DC or AC motor, paired with a feedback device and a sophisticated servo controller. The result is a compact, high-performance solution capable of delivering forceful, accurate movements in demanding industrial applications.
What sets high torque servo motors apart is their ability to maintain high torque even at low speeds. This feature makes them ideal for tasks that require both strength and finesse such as robotic arms lifting heavy components, or CNC machines executing delicate yet forceful cuts.

Key Features:
- Closed-loop control for real-time position and speed adjustments
- High torque density for powerful performance in compact form factors
- Precision motion control, even under varying load conditions
- Low vibration and noise, improving system stability and efficiency
- Energy-efficient operation with advanced thermal management
As industries demand faster, more precise, and more powerful motion systems, high torque servo motors have emerged as the go-to choice for engineers looking to optimize both control and output in complex automation environments.
Applications of High Torque Servo Motors
Thanks to their combination of precision, power, and responsiveness, high torque servo motors are used across a wide range of industries where motion control is mission-critical. Their ability to deliver consistent torque, even at low or variable speeds makes them the ideal choice for applications that demand both strength and accuracy.
1. Industrial Robotics
In robotic arms and automated handling systems, high torque servo motors provide the stability and force required to lift, move, and position heavy components with exceptional precision. Their fast response time ensures fluid, natural movements critical for assembly lines, welding robots, and pick-and-place operations.
2. CNC Machines and Metalworking
CNC milling, turning, and grinding machines require extremely accurate positioning to achieve tight tolerances. High torque servo motors enable these machines to perform rapid axis movements without compromising precision, even under the stress of cutting hard materials.
3. Automation and Packaging Lines
In packaging systems, high torque servo motors ensure smooth and synchronized operation of conveyors, labelers, and wrapping machines. Their ability to quickly start, stop, and reverse direction improves throughput while reducing mechanical wear.
4. Printing and Textile Machinery
Both industries demand high-speed, high-precision motion to control rollers, feeders, and print heads. Servo motors provide the torque stability and exact control needed to maintain consistent product quality, even at high volumes.
5. Medical and Laboratory Equipment
From surgical robots to automated analyzers, precision and reliability are non-negotiable in medical environments. High torque servo motors help drive delicate mechanisms with smooth motion and absolute control, reducing vibration and error margins.
6. Aerospace and Defense
Applications such as flight simulators, radar systems, and weapons guidance rely on high torque servo motors for exact positioning and high load-handling capacity, ensuring reliability in extreme conditions.
7. Electric Vehicles and AGVs
In autonomous guided vehicles (AGVs) and electric drivetrains, high torque servo motors contribute to responsive acceleration and dynamic load handling, essential for efficient and adaptive movement in logistics and warehousing.
By integrating high torque servo motors into these applications, industries benefit from increased efficiency, enhanced performance, and reduced downtime making them a cornerstone of modern motion control systems.
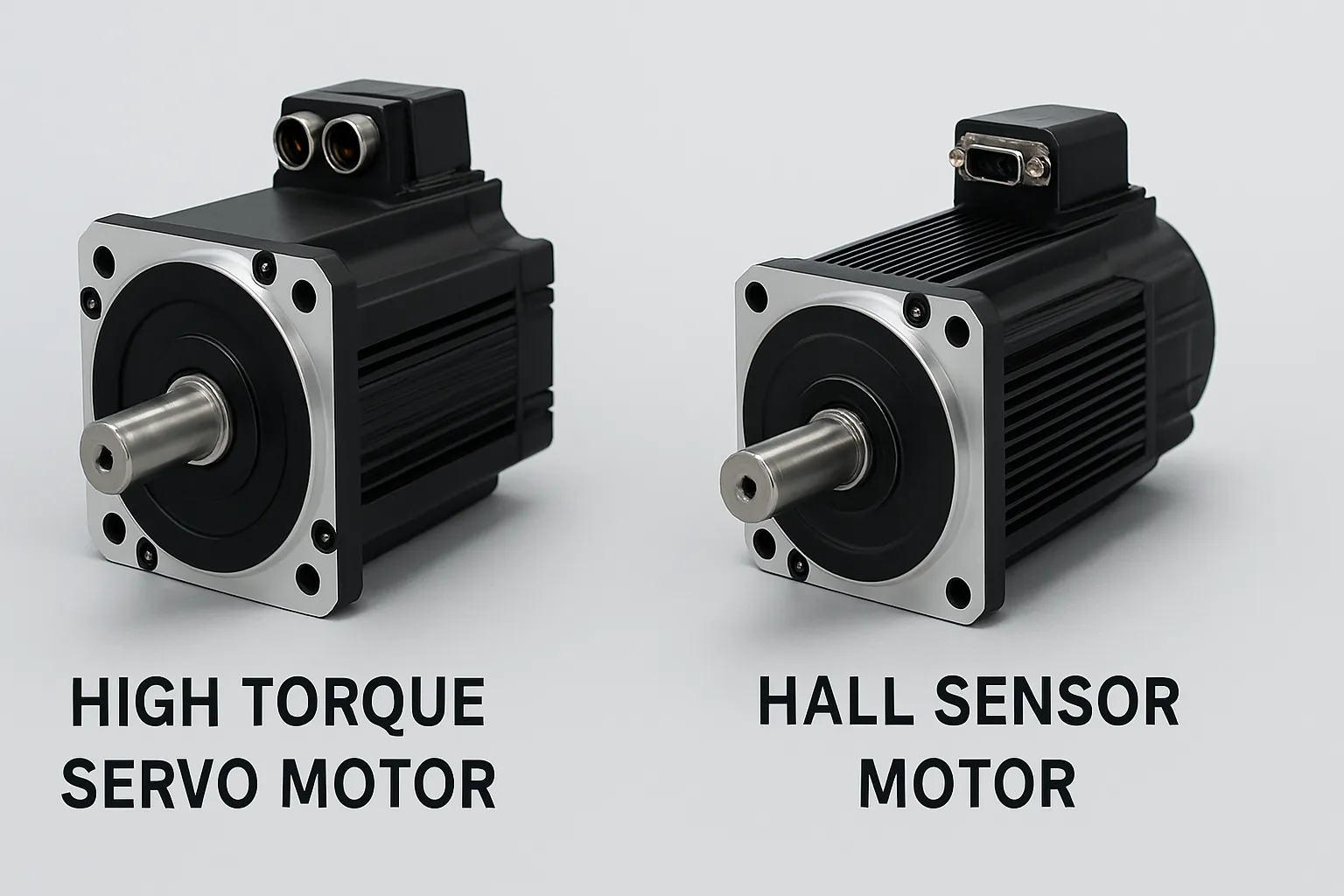
Key Differences Between High Torque Servo Motors and Hall Sensor Motors
While high torque servo motors are known for their advanced feedback control and precision, high torque Hall sensor motors take a simpler approach to motion control. These motors use Hall effect sensors to detect the position of the rotor, enabling basic feedback and commutation without the need for complex encoders or controllers.
What Are High Torque Hall Sensor Motors?
A Hall sensor is a device that responds to changes in magnetic fields. In motors, multiple Hall sensors are positioned inside the motor casing to detect the rotor’s magnetic orientation. Based on these readings, the controller determines when to energize the motor windings, allowing for basic position and speed control.
High torque Hall sensor motors typically belong to the brushless DC motor (BLDC) family, and while they may not match the ultra-precise control of servo motors, they still provide strong torque output, good reliability, and cost efficiency especially in applications where pinpoint accuracy is not a top priority.
High Torque Servo Motors vs. Hall Sensor: A Closer Look at Their Differences
The key distinction between high torque servo motors and high torque Hall sensor motors lies in the level of control and feedback they provide.
1. Control and Feedback Mechanism
The most significant difference lies in how each motor type manages motion control. High torque servo motors operate using a closed-loop system with encoders that continuously monitor the motor’s position, speed, and torque. This allows the system to make real-time adjustments for precise movement.
In contrast, Hall sensor motors use a simpler open-loop or semi-closed loop system. They rely on magnetic field readings from Hall sensors to determine the rotor’s position. This feedback is less detailed and results in lower accuracy compared to servo motors.
2. Precision and Accuracy
Servo motors are built for high-precision tasks. With encoder feedback, they can execute even the smallest angular changes with great consistency. That’s why they are commonly used in robotic arms, CNC systems, and automation tasks where precision is non-negotiable.
Hall sensor motors, while still capable of decent positional control, offer only moderate accuracy. Their feedback resolution is lower, which makes them suitable for simpler movements, especially where high precision isn’t critical.
3. Response to Load Changes
When the load on a motor suddenly changes, a servo motor can instantly adjust its output thanks to its continuous feedback loop. This ensures torque remains stable and performance stays consistent.
Hall sensor motors, however, tend to lag in dynamic adaptability. Since their feedback is limited, they may struggle to maintain torque or speed under fluctuating load conditions.
4. Setup Complexity and Maintenance
Servo systems require more sophisticated setup. They need specific servo drives, tuning, and sometimes programming to match the motor with the application. This increases both installation time and technical know-how.
Hall sensor motors are generally plug-and-play, requiring minimal configuration. Their simpler design also means they usually require less maintenance over time.
5. Cost and Budget Consideration
With greater control comes greater cost. Servo motors tend to be more expensive, not just in terms of the motor itself, but also due to the need for dedicated controllers and high-resolution encoders.
Hall sensor motors are more budget-friendly, making them a popular choice for cost-sensitive applications where ultra-precise control isn’t required.
6. Ideal Use Cases
Use servo motors when you need:
- Accurate positioning
- Fast response to load or direction changes
- High-end industrial automation or robotics
Use Hall sensor motors when you need:
- Basic torque and speed control
- Cost-effective solutions
- Simpler, repetitive motion in fixed-speed systems
Ultimately, the choice between a high torque servo motor and a Hall sensor motor depends on what your application demands. If your system requires pinpoint accuracy, fast response, and real-time adaptability, then a high torque servo motor is the clear winner. But if your focus is on cost-efficiency, ease of use, and sufficient torque for less complex operations, a Hall sensor motor may be the more practical solution.
How to Choose the Right High Torque Servo Motors?
Selecting the right high torque servo motor for your application isn’t just about picking the most powerful model. It requires a careful evaluation of technical requirements, environmental factors, and performance goals.

Here are the key criteria to consider:
1. Define Your Torque and Speed Requirements
Start by determining the torque you need at both peak and continuous levels. Also, assess the speed range your application requires. Some systems demand high torque motors at low speeds (e.g., lifting systems), while others need consistent torque across a wide RPM range (e.g., conveyor belts).
Choosing a servo motor that matches these parameters ensures optimal efficiency and avoids over-specification or underperformance.
2. Consider Load Characteristics
Understanding your load is critical. Ask yourself:
- Is the load constant or variable?
- Does it involve frequent start-stop motion or direction changes?
- Are there any shock loads?
For dynamic or complex loads, you’ll need a servo motor with fast acceleration, high peak torque, and strong feedback control to maintain stability and precision.
3. Evaluate Feedback and Positioning Needs
If your application demands high-precision positioning or real-time closed-loop control, choose a servo motor with a high-resolution encoder.
Applications like CNC machining or robotic joints benefit from precise positional feedback, while lower-end applications may function well with a mid-resolution option.
4. Check Compatibility with Drive Systems
Your servo motor must work seamlessly with your servo drive or motion controller. Check communication protocols (e.g., EtherCAT, CANopen), voltage requirements, and feedback interfaces. ITG, for example, offers motors designed to integrate easily with a wide range of servo drives for industrial use.
5. Analyze Physical Constraints
Don’t overlook the size, mounting style, and form factor. Whether your machine has space limitations or specific orientation requirements, the physical fit of the servo motor should match your mechanical design without modification.
Also, considering thermal conditions does the motor need to operate in a hot, enclosed, or vibration-prone environment? If so, thermal protection, IP ratings, and vibration resistance are important factors.
6. Prioritize Energy Efficiency
Modern high torque servo motors can be highly energy efficient, which reduces operating costs in the long run. Look for models with optimized winding designs and advanced thermal management to minimize energy waste, especially in 24/7 production lines.
Finally, choose a supplier or manufacturer with strong engineering support, proven product quality, and long-term availability. A trusted partner like ITF can help assess your technical needs and recommend the best-fit servo motor from their product range backed by expert consultation and service.
By carefully matching performance specifications with application needs, you can select a high torque servo motor that enhances productivity, improves motion accuracy, and lowers maintenance over time.
Conclusion
When it comes to delivering power, precision, and performance, high torque servo motors consistently outpace their Hall sensor counterparts in demanding industrial applications. While Hall sensor motors remain a practical choice for simpler, cost-sensitive systems, they simply can’t match the accuracy, responsiveness, and control of servo technology.
By understanding the key differences between the two motor types and carefully evaluating your system’s torque, speed, and feedback needs, you can make a well-informed decision that aligns with both your technical goals and budget.

