In today’s rapidly evolving industrial landscape, motion control systems play a critical role in determining the efficiency, precision, and reliability of modern machines. As industries demand higher performance with lower energy consumption and minimal maintenance, traditional motor technologies are no longer sufficient. This is where the Brushless DC motor (BLDC) emerges as a powerful solution. Known for its high efficiency, precise control, and long service life, the BLDC motor has become a cornerstone in automation, robotics, and advanced linear motion systems. In this article by ITG, we will explore what a brushless DC motor is, how it works, and why it is increasingly essential in high-performance industrial applications.
What Is a Brushless DC Motor?
A Brushless DC motor (BLDC motor) is an electrically powered motor that converts direct current (DC) electrical energy into mechanical motion without using brushes or a mechanical commutator. Instead of relying on physical contact to switch current flow, a BLDC motor uses electronic commutation, controlled by an external drive or controller, to precisely energize the stator windings.
At its core, a BLDC motor consists of a stator with multiple windings and a rotor equipped with permanent magnets. When the controller sequentially supplies current to the stator phases, it generates a rotating magnetic field that interacts with the rotor magnets, causing smooth and continuous rotation. This contactless operating principle significantly reduces mechanical wear and energy loss.
Unlike traditional brushed DC motors, where brushes and commutators are subject to friction, sparking, and frequent maintenance, brushless DC motors deliver higher efficiency, longer lifespan, and more reliable performance. The absence of brushes eliminates electrical noise and heat generated by mechanical contact, making BLDC motors particularly suitable for high-speed, high-precision, and continuous-duty applications.
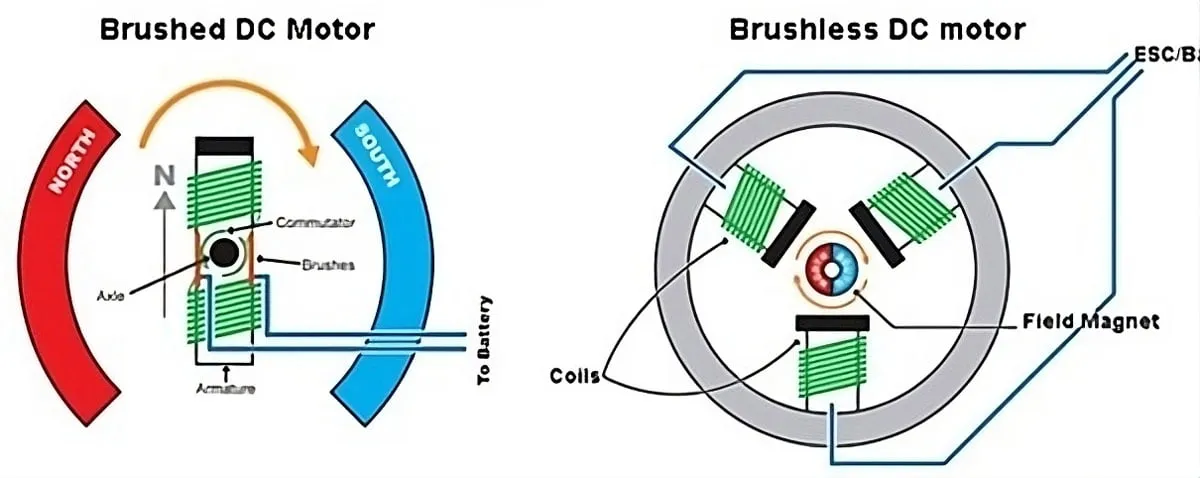
Another defining feature of brushless DC motors is their advanced controllability. By adjusting the switching sequence and current supplied by the electronic controller, engineers can accurately regulate speed, torque, and position. This level of control allows BLDC motors to seamlessly integrate into modern automation systems, robotics, CNC machinery, and linear motion platforms.
In essence, a brushless DC motor combines the simplicity of DC power with the performance advantages of electronically controlled commutation. This makes it a preferred motor technology for industries that require precision motion, energy efficiency, and long-term operational stability, setting the foundation for its widespread adoption in advanced industrial and linear motor solutions.
Main Components of a Brushless DC Motor
To fully understand how a brushless DC motor delivers high efficiency and precise motion control, it is essential to examine its core components. Unlike brushed motors, BLDC motors rely on a carefully coordinated interaction between mechanical parts and electronic systems. Each component plays a critical role in ensuring smooth operation, reliability, and long service life.
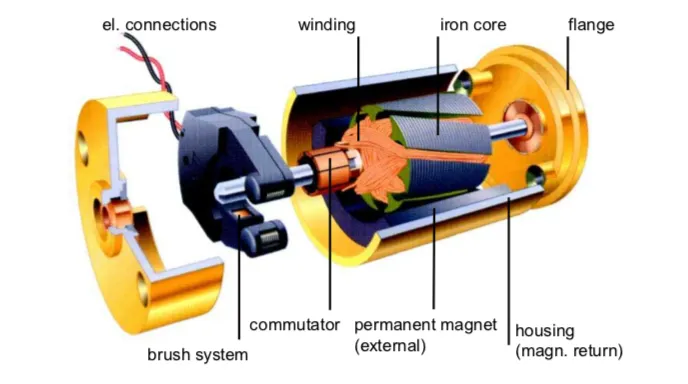
Stator
The stator is the stationary part of a brushless DC motor and is responsible for generating the rotating magnetic field. It is composed of laminated steel cores with multiple copper windings arranged in phases. When electrical current flows through these windings, according to signals from the electronic controller, the stator produces a controlled magnetic field that drives the rotor’s motion.
The design and quality of the stator directly influence the motor’s efficiency, torque output, and thermal performance. In industrial-grade BLDC motors, optimized stator geometry and high-quality insulation help minimize energy loss while supporting continuous operation under demanding conditions.
Rotor
The rotor is the rotating component of a BLDC motor and is typically equipped with permanent magnets mounted either on the surface or embedded within the rotor core. These magnets interact with the stator’s magnetic field, generating torque and causing the rotor to spin.
Compared to brushed motors, the rotor in a BLDC motor experiences less heat buildup because no current flows through it. This contributes to higher efficiency, improved power density, and greater durability, key advantages for applications requiring high-speed rotation and precise motion control.
Electronic Speed Controller (ESC)
The electronic speed controller (ESC) is a defining element of brushless DC motor technology. It replaces the mechanical commutator and brushes found in traditional DC motors by electronically switching the current between stator phases. The ESC determines the timing, sequence, and magnitude of current, enabling accurate control of motor speed and torque.
Through advanced control algorithms, the ESC allows BLDC motors to operate smoothly across a wide speed range while maintaining high efficiency. This electronic commutation is also what enables seamless integration of BLDC motors into modern automation, robotics, and linear motion systems.
Position Sensors (or Sensorless Control)
To ensure precise commutation, many BLDC motors use position sensors, such as Hall effect sensors, to detect the rotor’s angular position. These sensors provide real-time feedback to the controller, allowing accurate phase switching, especially at low speeds or during startup.
In some applications, sensorless BLDC motors are preferred. These motors estimate rotor position based on back electromotive force (back-EMF), reducing system complexity and cost. The choice between sensored and sensorless control depends on the required precision, operating speed range, and application environment.
Together, these core components form a highly efficient and reliable motor system. The seamless interaction between the stator, rotor, controller, and feedback mechanism is what enables brushless DC motors to deliver superior performance in demanding industrial and linear motion applications, setting the stage for understanding how BLDC motors actually work in operation.
How Does a Brushless DC Motor Work?
A brushless DC motor operates based on the principle of electronic commutation, where the switching of current in the motor windings is controlled electronically rather than mechanically. This approach allows the motor to achieve smooth rotation, high efficiency, and precise control, key requirements in modern industrial and linear motion applications.
Step 1: Power Supply and Control Signals
The operation of a BLDC motor begins when DC power is supplied to the electronic speed controller (ESC). The controller acts as the “brain” of the system, interpreting control inputs such as speed, torque, or position commands from the drive system or motion controller.
Based on these inputs, the ESC determines which stator windings should be energized and in what sequence. This decision-making process is continuous and happens in real time, ensuring accurate motor response under varying load conditions.
Step 2: Creation of a Rotating Magnetic Field
Once the controller energizes the stator windings, a magnetic field is generated within the stator. By sequentially switching the current between different phases, the controller creates a rotating magnetic field around the stator.
This electronically generated rotating field replaces the mechanical commutation found in brushed motors, eliminating physical contact and significantly reducing friction and energy loss.
Step 3: Rotor Alignment and Motion
The permanent magnets on the rotor naturally attempt to align with the rotating magnetic field produced by the stator. As the stator field continues to rotate, the rotor follows, resulting in continuous and smooth rotational motion.
Torque is generated through the interaction between the stator’s electromagnetic field and the rotor’s magnetic field. The strength of this interaction and therefore the torque output, depends on the current supplied by the controller.
Step 4: Rotor Position Feedback and Commutation Timing
To maintain optimal performance, the controller must know the rotor’s position at all times. This is achieved either through position sensors (such as Hall effect sensors) or through sensorless control techniques that estimate rotor position using back electromotive force (back-EMF).
Accurate rotor position information allows the controller to precisely time the commutation process, ensuring efficient torque production and smooth operation across different speeds, including startup and low-speed conditions.
Step 5: Speed and Torque Regulation
By adjusting the switching frequency and current amplitude, the controller can precisely regulate the motor’s speed and torque. This enables BLDC motors to respond quickly to changes in load or command signals, making them ideal for applications that demand dynamic performance and high positional accuracy.
Advanced control algorithms also help optimize efficiency, reduce noise, and maintain stable operation under continuous or high-duty-cycle use.
In summary, a brushless DC motor works by combining electronic commutation, real-time feedback, and precise current control to produce smooth and efficient motion. This sophisticated operating principle is what allows BLDC motors to outperform traditional brushed motors and makes them a critical component in advanced automation, robotics, and linear motion systems used across modern industries.
Types of Brushless DC Motors
Brushless DC motors are available in a variety of configurations, each designed to meet specific performance, control, and application requirements. Understanding the different types of BLDC motors helps engineers and system designers select the most suitable solution for their motion and automation systems.
- Inner Rotor Brushless DC Motors: In this design, the rotor is positioned inside the stator, allowing the motor to achieve high rotational speeds and fast dynamic response. Inner rotor BLDC motors typically have lower rotational inertia, making them ideal for applications that require rapid acceleration and precise speed control, such as robotics, CNC machinery, and high-performance motion systems.
- Outer Rotor Brushless DC Motors: With the rotor located on the outside of the stator, this motor type delivers higher torque at lower speeds. The increased rotor diameter enhances torque production and smooth operation, making outer rotor BLDC motors well-suited for conveyors, fans, compact drive units, and space-constrained industrial designs.
- Sensored Brushless DC Motors: These motors integrate Hall effect sensors to provide accurate rotor position feedback to the controller. This enables smooth startup, stable low-speed operation, and precise commutation. Sensored BLDC motors are commonly used in applications that demand high positioning accuracy and consistent torque, including automation equipment and linear motion platforms.
- Sensorless Brushless DC Motors: Sensorless BLDC motors eliminate physical position sensors by estimating rotor position through back electromotive force (back-EMF). This approach reduces system complexity and improves reliability, particularly in harsh or high-speed environments. Sensorless designs are often chosen for applications where simplicity, durability, and cost efficiency are key considerations.
- Single-Phase and Three-Phase BLDC Motors: Three-phase BLDC motors are the standard choice for industrial applications due to their smooth torque output, higher efficiency, and better controllability. Single-phase versions, while less common, are used in lower-power systems where simplified control is sufficient.
Together, these BLDC motor types provide engineers with a wide range of design options. By carefully evaluating factors such as speed, torque, control precision, and operating conditions, manufacturers can select the most appropriate brushless DC motor to achieve optimal performance in automation, motion control, and linear motor systems.
Industrial Applications of Brushless DC Motors
Thanks to their high efficiency, precise controllability, and long operational life, brushless DC motors are widely adopted across a broad range of industrial sectors. Their ability to deliver reliable performance under demanding conditions makes them a core component in modern automation and motion control systems.
- Industrial Automation and Robotics: BLDC motors are extensively used in robotic arms, pick-and-place systems, and automated assembly lines where high precision, fast response, and repeatable motion are essential. Their smooth torque output and accurate speed control enable consistent performance in continuous and high-duty-cycle operations.
- Linear Motion Systems and Actuators: In linear stages, actuators, and positioning systems, brushless DC motors provide the dynamic performance and control accuracy required for precise linear movement. When combined with advanced drives and feedback systems, BLDC motors support applications such as semiconductor manufacturing, inspection equipment, and precision motion platforms.
- CNC Machines and Manufacturing Equipment: CNC tools and industrial machinery rely on BLDC motors for stable speed control, high efficiency, and reduced maintenance. Their ability to operate at high speeds with minimal vibration improves machining accuracy, surface finish, and overall productivity.
- Medical and Laboratory Equipment: In medical devices and laboratory instruments, BLDC motors are valued for their low noise, reliability, and smooth operation. Applications include diagnostic equipment, pumps, imaging systems, and precision instruments where consistent performance and minimal downtime are critical.
- Electric Vehicles, AGVs, and Mobile Robots: Brushless DC motors are widely used in electric vehicles, automated guided vehicles (AGVs), and mobile robots due to their high power density and energy efficiency. These characteristics help extend battery life while delivering the torque and responsiveness required for transportation and material handling tasks.
- Aerospace and High-Tech Industries: In aerospace and advanced technology sectors, BLDC motors are selected for their lightweight design, high efficiency, and exceptional reliability. They are commonly found in actuators, control systems, and equipment where performance and durability are non-negotiable.
Overall, the versatility of brushless DC motors allows them to meet the diverse requirements of modern industry. From precision automation to advanced linear motion systems, BLDC motors continue to play a vital role in enabling efficient, accurate, and reliable industrial solutions.
Conclusion
Brushless DC motors have become a cornerstone of modern motion control technology, redefining how industries approach efficiency, precision, and long-term reliability. By eliminating mechanical commutation and leveraging advanced electronic control, BLDC motors deliver superior performance, reduced maintenance, and exceptional controllability across a wide range of operating conditions.
From industrial automation and robotics to CNC machinery and advanced linear motion systems, the flexibility of brushless DC motors enables engineers to design solutions that are faster, more accurate, and more energy-efficient. Their ability to seamlessly integrate with intelligent drives and feedback systems makes them an ideal choice for applications where precision and dynamic response are critical.

