Ever wondered how electric cars accelerate so smoothly, industrial robots move with pinpoint accuracy, or wind turbines generate energy so efficiently? The secret lies in a special type of motor called the Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor (PMSM). Known for its exceptional efficiency, durability, and impressive energy savings, the PMSM is becoming the “heart” of many modern technologies. In this article, we’ll explore how it works, its structure, and why it’s the preferred choice across industries.
What is a Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor?
A Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor (PMSM) is a type of AC motor that uses permanent magnets embedded in or attached to its rotor to create a constant magnetic field. Unlike induction motors, which rely on current induced in the rotor windings to generate a magnetic field, PMSMs use high-strength magnets often made from rare-earth materials like neodymium to maintain rotor magnetism without the need for electrical excitation.
The term “synchronous” refers to the fact that the rotor and the stator’s rotating magnetic field move at the same speed, ensuring precise control over torque and position. This synchronous operation, combined with the use of permanent magnets, results in superior energy efficiency, high power density, and consistent performance across a wide range of operating conditions.
PMSMs have gained significant attention in recent years thanks to their ability to deliver high torque at low speeds, operate quietly, and maintain efficiency even under heavy loads. From electric vehicles to high-performance industrial machinery, the permanent magnet synchronous motor is increasingly becoming the go-to choice for engineers seeking performance and reliability.
How Does a Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Work?
The operation of a permanent magnet synchronous motor is based on the interaction between the magnetic field of the rotor’s permanent magnets and the rotating magnetic field generated by the stator windings.
When a three-phase AC current flows through the stator, it produces a rotating magnetic field. The permanent magnets on the rotor are attracted to this field, causing the rotor to turn at the exact same speed hence the term “synchronous.”
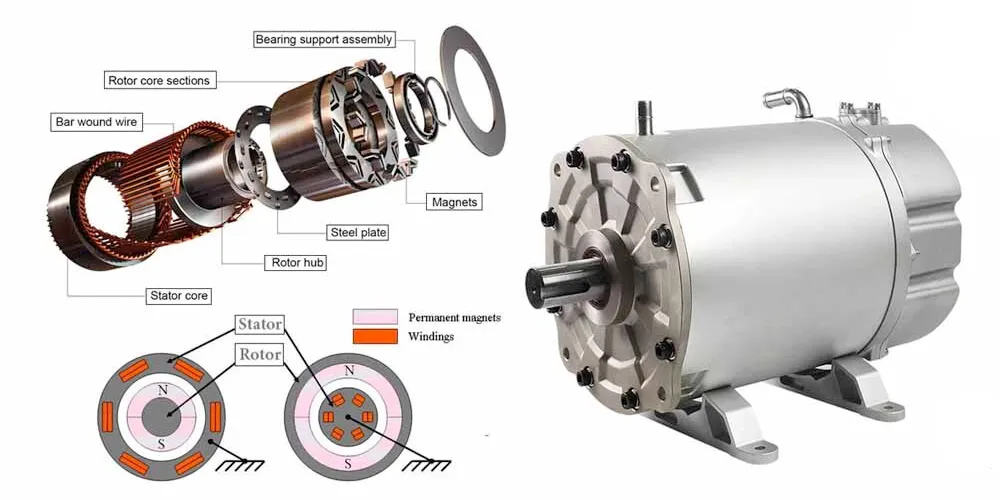
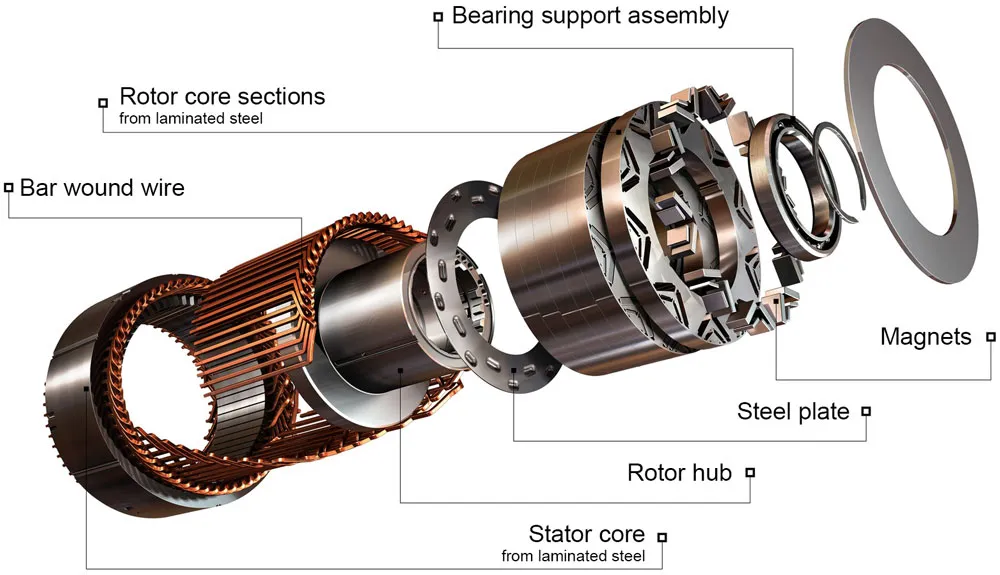
1. Structure of a PMSM
- Rotor: Contains high-strength permanent magnets (such as neodymium or samarium-cobalt) that produce a constant magnetic field.
- Stator: Houses copper windings that carry alternating current to generate a rotating magnetic field.
- Position Sensors: Devices like encoders or resolvers are often used for precise control of rotor position, essential in applications requiring high accuracy.
2. Operating Principle
- Current Input: A three-phase AC supply energizes the stator windings.
- Magnetic Field Creation: The energized stator produces a rotating magnetic field.
- Synchronous Rotation: The rotor’s permanent magnets lock onto the stator’s field, rotating at the same speed without slip.
- Torque Generation: The interaction between the stator field and the rotor’s magnetic field produces continuous torque output.
Unlike induction motors, PMSMs do not suffer from slip losses, allowing them to operate with higher efficiency and better torque control. Additionally, the absence of rotor windings reduces heat generation and minimizes maintenance needs.
Types of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors
Although all permanent magnet synchronous motors operate on the same fundamental principle, their rotor design can vary significantly. The two most common types are Surface-Mounted PMSM and Interior PMSM, each optimized for different performance requirements.
1. Surface-Mounted PMSM (SPMSM)
In a surface-mounted design, the permanent magnets are fixed directly onto the surface of the rotor.
- Advantages:
- Simple rotor construction.
- Low manufacturing cost compared to other PMSM types.
- Excellent efficiency at low to medium speeds.
- Disadvantages:
- Lower mechanical strength due to exposed magnets.
- Limited ability to handle high-speed operations.
Typical Applications: Low- to medium-speed electric drives, pumps, fans, and general-purpose industrial equipment.
2. Interior PMSM (IPMSM)
In an interior design, the permanent magnets are embedded inside the rotor. This structure allows for both magnetic torque and reluctance torque generation.
- Advantages:
- Higher mechanical strength, making it suitable for high-speed operations.
- Better torque density and efficiency over a wider speed range.
- Improved protection for magnets from mechanical damage.
- Disadvantages:
- More complex and expensive to manufacture.
- Requires precise design and control strategies.
Typical Applications: Electric vehicles, high-performance industrial machinery, and servo drive systems.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors
When evaluating a permanent magnet synchronous motor (PMSM) for a project, it’s important to understand both its strengths and its limitations. This balanced perspective ensures the chosen motor aligns with the technical, economic, and operational requirements of the application.
Advantages of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors
PMSMs offer several benefits that make them increasingly popular in modern engineering:
1. High Efficiency: The rotor’s magnetic field is generated by permanent magnets, eliminating the slip losses present in induction motors. This results in efficiencies often exceeding 90%.
2. High Power Density: The use of rare-earth magnets enables PMSMs to deliver high torque output relative to their size, making them ideal for space-constrained designs.
3. Precise Torque and Speed Control: Because the rotor rotates in perfect synchrony with the stator’s magnetic field, PMSMs can achieve highly accurate torque control, which is crucial in robotics, CNC machines, and EVs.
4. Quiet and Smooth Operation: Lower vibration and noise levels improve user comfort and reduce wear on connected components.
5. Low Maintenance Requirements: Without brushes or rotor windings, PMSMs generate less heat and experience fewer mechanical failures, extending their service life.
In summary, these advantages explain why PMSMs are a preferred choice in applications demanding efficiency, precision, and long-term reliability.
Disadvantages of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors
Despite their strengths, PMSMs are not without challenges:
1. Higher Initial Cost: Permanent magnets, particularly those made from neodymium or samarium-cobalt, are costly and contribute to a higher purchase price.
2. Temperature Sensitivity: High operating temperatures can weaken the magnetic field, reducing motor performance over time.
3. Complex Contrensitivity: PMSMs require sophisticated controllers and position sensors, increasing the system’s overall cost and complexity.
4. Risk of Demagensitivity: Excessive heat, overcurrent, or mechanical stress can permanently damage the magnets.
In conclusion, while PMSMs deliver exceptional performance and efficiency, their higher costs and control requirements mean they are best suited for applications where these benefits outweigh the trade-offs.
Applications of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors
Thanks to their high efficiency, precision control, and compact design, permanent magnet synchronous motors (PMSMs) have found their way into a wide variety of industries. From powering electric cars to driving industrial automation, PMSMs are a key enabler of modern technology.
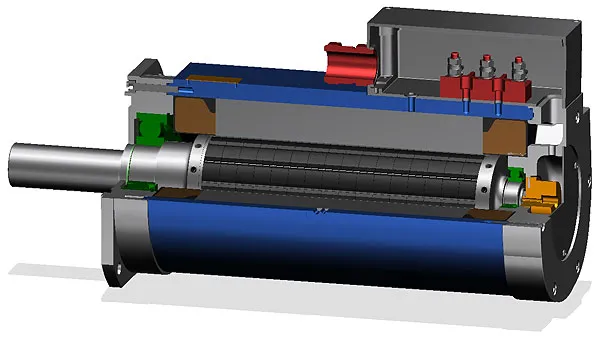
1. Electric Vehicles (EVs) and Hybrid Cars
PMSMs are widely used in the automotive industry because of their ability to deliver high torque at low speeds, maintain efficiency across a broad speed range, and operate quietly. These characteristics make them ideal for EVs and hybrid powertrains, where energy efficiency directly impacts driving range.
2. Industrial Automation and Robotics
In manufacturing, PMSMs drive robotic arms, CNC machines, and conveyor systems with unmatched precision. Their synchronous operation ensures accurate positioning, which is critical for automated assembly lines and high-precision machining.
3. HVAC Systems
Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems benefit from PMSMs’ high efficiency and low noise levels. By reducing energy consumption, PMSMs help lower operational costs and contribute to greener building solutions.
4. Renewable Energy Systems
In wind turbines and hydroelectric generators, PMSMs are used to convert mechanical energy into electrical power with minimal loss. Their robust design allows them to withstand fluctuating loads while maintaining efficiency.
5. Aerospace and Marine Applications
From propulsion systems in ships to specialized equipment in aircraft, PMSMs are valued for their reliability, high power density, and reduced maintenance needs in challenging environments.
Conclusion
The permanent magnet synchronous motor is more than just another electric motor, it’s a driving force behind the technological shift toward greater efficiency, precision, and sustainability.
By combining the power of rare-earth magnets with synchronous operation, PMSMs deliver performance levels that traditional motors struggle to match. From electric vehicles and renewable energy systems to industrial automation and aerospace applications, their versatility knows no bounds.
It is also worth noting that PMSM technology forms the basis for other advanced motor types, such as Linear Motors, which provide direct linear motion without mechanical transmission, and Torque Motors, which deliver high torque at low speeds for applications requiring direct-drive performance. Together, these technologies illustrate how permanent magnet based designs are shaping the future of efficient, intelligent, and versatile drive systems.

