From smart factories to surgical robotics, the linear motion industry is at the core of modern innovation. As industries demand faster, more precise, and more efficient systems, linear motion technology has evolved from basic mechanical parts into intelligent, data-driven platforms.
This article dives into the key products, powerful applications, and disruptive trends that are redefining how motion is engineered, delivered, and scaled across sectors. If you’re building for the future, it starts here with motion that thinks, adapts, and delivers real results.
Overview of the Linear Motion Industry
What is Linear Motion?
Linear motion refers to movement in a straight line, as opposed to rotational or curved paths. In industrial settings, linear motion systems are mechanical or electromechanical solutions designed to guide and control this precise motion with high accuracy, speed, and repeatability.
These systems typically include components such as linear guides, actuators, bearings, and motors all working together to perform smooth and controlled linear movements.
But what is linear motion beyond the textbook definition? It’s the lifeblood of modern automation. It’s what allows robotic arms to glide with micron-level precision, medical scanners to move seamlessly, and semiconductor devices to operate at unimaginable scales.
Without linear motion technology, the entire framework of industrial progress would collapse. It’s not just engineering its precision in motion, profit in execution, and scalability by design.
A Brief History and Evolution
The origins of linear motion can be traced back to early mechanical devices, primitive tracks, pulleys, and screw mechanisms that allowed for rudimentary straight-line movement. But it wasn’t until the industrial revolution that linear motion systems began to evolve into precise engineering solutions.
- 20th Century: Introduction of ball screws, slide rails, and pneumatic actuators. Motion became faster, smoother, more controlled.
- 2000s: The fusion of electronics and mechanics gave rise to mechatronic systems, where sensors, motors, and controllers worked as a unified force.
- Today: With the rise of Industry 4.0, linear motion technology has entered its golden era. We’re talking AI-enhanced drives, IoT-connected systems, ultra-lightweight materials, and self-monitoring actuators.
From simple rails to smart, adaptive motion platforms the evolution of linear motion reflects the relentless push for speed, precision, and intelligence.
Why is Linear Motion Important in Modern Industries?
In today’s high-demand, fast-paced industrial world, precision, reliability, and efficiency are non-negotiable. This is exactly where the linear motion industry dominates.
From manufacturing to healthcare, from logistics to electronics linear motion systems are enabling breakthroughs across sectors:
- Manufacturing: Increase productivity with automated assembly lines driven by electric actuators and smart guides.
- Medical Devices: Achieve exceptional accuracy in imaging and diagnostics with low-noise, high-precision motion.
- Semiconductors: Scale nanometer-level production while ensuring zero compromise in repeatability.
- E-commerce & Packaging: Handle massive order volumes with conveyor systems and robotic pickers powered by linear motion technology.
The linear motion industry is more than a niche, it’s a $10+ billion ecosystem powering the core of Industry 4.0. As global industries shift toward smart automation and data-driven control, linear motion systems are becoming foundational tools for success.
Key Products and Technologies in the Industry
Common Linear Motion Components
At the heart of the linear motion industry lies a set of core components that power precision across manufacturing, healthcare, electronics, and more. These are not just parts, they are profit-driving mechanisms engineered for performance.
1. Linear Guideways: Enable smooth, straight-line motion under heavy loads with minimal friction. Critical for applications demanding high stability and repeatability.
2. Linear Actuators: Convert electrical or pneumatic energy into precise motion. Electric actuators, in particular, offer programmable accuracy and faster response times.
3. Linear Motors: Deliver high-speed, direct-drive motion without mechanical transmission losses. Ideal for cleanroom environments, semiconductor lines, and automated labs.
4. Ball Screws & Lead Screws: Offer efficient load transmission with minimal backlash perfect for CNC machinery and robotic arms.
5. Motion Controllers & Encoders: The brains behind the movement, syncing data and commands in real-time for flawless control.

Understanding what is linear motion means recognizes how these components operate in synergy to turn static systems into dynamic value generators.
Innovations Driving the Industry
The linear motion technology of today is smarter, faster, and radically more compact than ever before. We’re no longer in the era of heavy mechanical parts, we’re in the age of miniaturized innovation.
- Miniaturization: Modern systems are becoming smaller, lighter, and more agile without sacrificing performance. This allows motion systems to be integrated into microsurgical tools, lab automation equipment, and compact robots.
- Modular Smart Systems: Pre-assembled motion modules now combine motors, drives, sensors, and controllers in one unit cutting design time and boosting deployment speed.
- Wireless Diagnostics & Self-Tuning: Embedded intelligence allows linear systems to detect anomalies, auto-calibrate, and optimize in real-time zero downtime, zero guesswork.
Role of AI and IoT in Motion Systems
- AI Algorithms: Predict wear, optimize motion paths, and enhance energy efficiency without human intervention. AI-powered drives can even adapt to unexpected shifts in load or speed on the fly.
- IoT Connectivity: Sensors embedded into linear actuators and motors stream real-time data to the cloud or edge devices allowing predictive maintenance, remote diagnostics, and seamless integration into Industry 4.0 ecosystems.
- Digital Twins & Simulation: AI models create exact virtual replicas of motion systems to test scenarios, optimize usage, and reduce failure risk.
These aren’t future trends. They’re now-essential components of every competitive linear motion strategy.
Sustainability and Material Advancements
- Lightweight Composites: Carbon fiber and engineered plastics are replacing heavy metal components, reducing energy consumption and enhancing machine speed.
- Low-Friction Coatings: Advanced surface treatments extend the life of linear guides and actuators while reducing lubrication needs good for machines, better for the planet.
- Eco-Friendly Design: Compact, modular systems reduce material waste, streamline logistics, and lower carbon footprints throughout the product lifecycle.
As regulations tighten and markets demand greener operations, the linear motion industry is adapting fast, delivering sustainable innovation that doesn’t cut performance.
Applications and Use Cases of Linear Motion Systems
From powering smart factories to enabling microscopic surgical tools, linear motion systems are embedded in the heart of modern innovation.
Let’s break down where the impact hits hardest and why these systems are no longer optional, but mission-critical.
Manufacturing & Industrial Automation
The linear motion industry delivers the speed, precision, and repeatability that modern production demands.
- Robotic Arms & CNC Machines: Linear actuators and motors control tool paths with sub-millimeter accuracy, drastically improving machining efficiency.
- Automated Assembly Lines: Guideways and linear slides move parts through production stations seamlessly cutting cycle times and reducing human error.
- Pick-and-Place Systems: High-speed linear drives enable rapid component handling, improving throughput across electronics, packaging, and consumer goods.
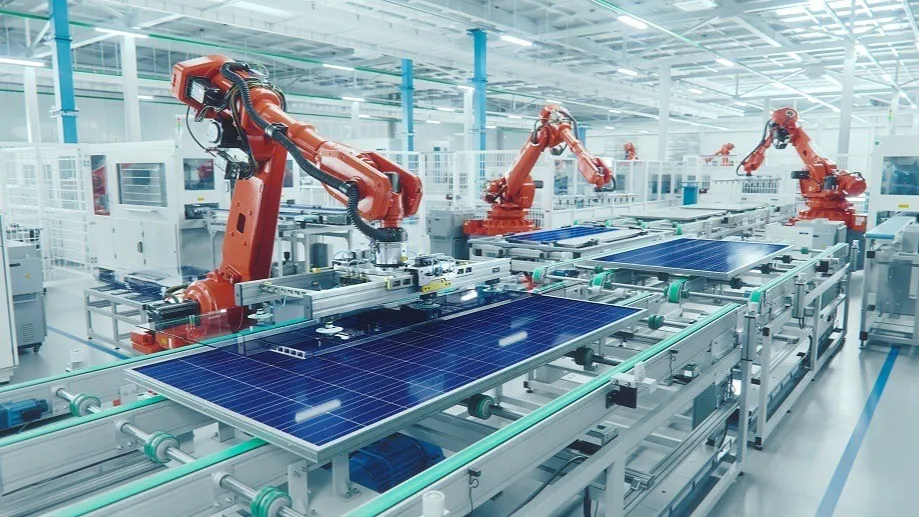

Semiconductor and Electronics
In the semiconductor and electronics industries, what is linear motion? It’s the foundation of cleanroom-compatible, vibration-free, high-speed automation.
- Wafer Inspection & Lithography: Ironless linear motors offer frictionless movement crucial for imaging systems and exposure tools operating at atomic-scale precision.
- Component Placement in PCB Assembly: Linear actuators deliver lightning-fast, pinpoint motion, boosting output without sacrificing placement accuracy.
- Microelectronics Testing Equipment: Quiet, stable motion platforms are essential for test reliability and data accuracy.
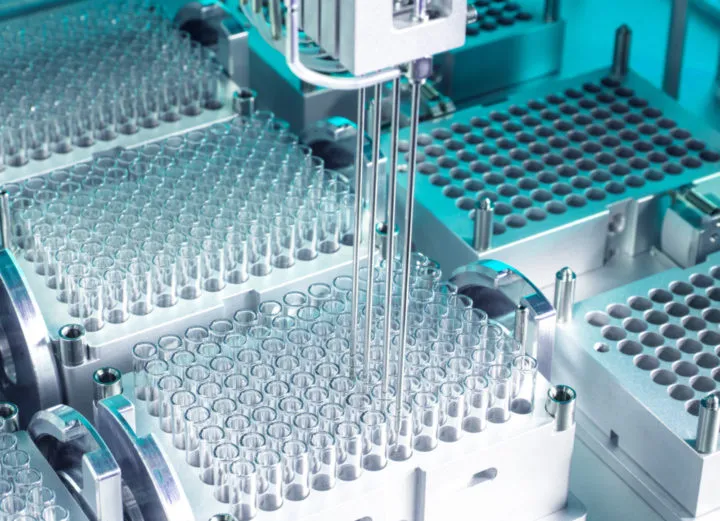
Healthcare and Laboratory Equipment
Precision isn’t just profitable, it’s life-saving. In the medical and lab fields, linear motion systems empower devices that diagnose, analyze, and even heal with silent, ultra-smooth precision.
- Medical Imaging: MRI beds, CT scanners, and X-ray arms rely on whisper-quiet, vibration-free motion for accurate scans and patient safety.
- Diagnostic Analyzers: Automated pipetting and sample-handling systems are powered by compact, reliable linear actuators.
- Surgical Robots & Lab Automation: Clean, compact, and sterile-ready components make linear motion technology the cornerstone of robotic precision medicine.

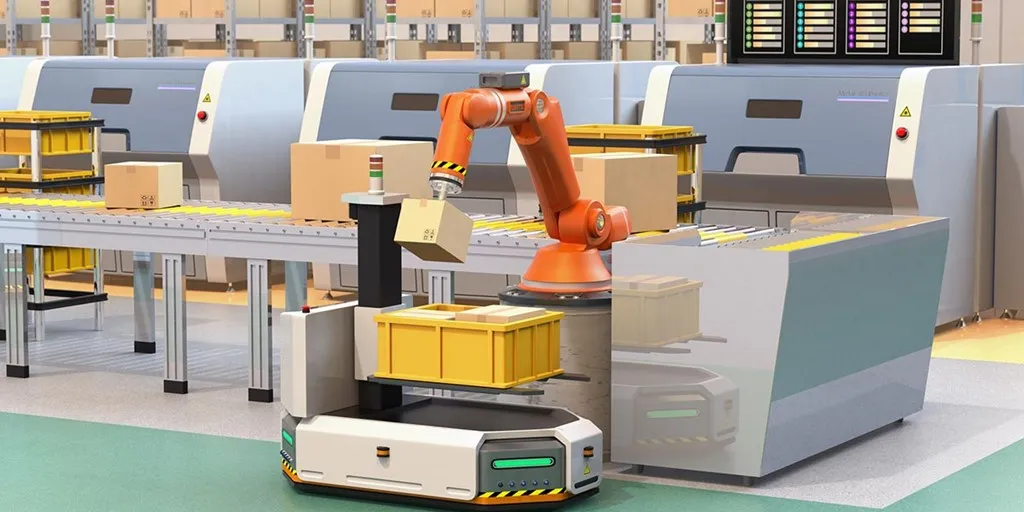
Logistics, Packaging, Printing, and Other Industries
High-volume, high-speed, high-demand: these are the defining traits of logistics and packaging environments and linear motion systems are engineered to thrive here.
- Conveyor and Sorting Systems: Linear actuators move packages at high speeds with zero deviation, even under continuous 24/7 workloads.
- Packaging Equipment: From sealing and filling to cutting and labeling, linear guides keep the process fast, synchronized, and flawless.
- Printing and Labeling Machines: Achieve crisp, distortion-free results with linear motion rails that maintain stability under high-speed operation.

Market Landscape and Future Trends
The linear motion industry isn’t just keeping pace, it’s setting the pace for industrial automation, precision engineering, and smart manufacturing worldwide.
Emerging Future Trends You Can’t Ignore
Current Market Analysis and Key Industry Players
As of now, the global linear motion industry is valued at over $10 billion, and it’s projected to grow at a CAGR of 5–7% over the next five years. What’s driving this surge? A global push for automation, labor efficiency, and ultra-precise manufacturing across sectors from automotive to semiconductors, life sciences to logistics.
1. Collaborative Robots (Cobots)
Cobots work side-by-side with humans and they demand compact, intelligent, and ultra-safe linear motion systems.
- Fast to deploy, ideal for SMEs
- Flexible for low-volume, high-mix production
- Built on responsive and precise motion components
2. Motion-as-a-Service (MaaS)
MaaS lets companies subscribe to motion systems, complete with service, upgrades, and analytics.
- Reduces upfront costs
- Converts CapEx to OpEx
- Accelerates automation for smaller firms
3. Real-Time Motion Analytics
Smart sensors now make linear motion systems more intelligent than ever.
- Predict issues before failure
- Boost energy and operational efficiency
- Improve quality and traceability
Top Challenges in the Linear Motion Industry
No industry scales without resistance. The linear motion systems market faces critical challenges that require bold action and innovation:
High Costs vs ROI Pressure
Advanced actuators, motors, and smart sensors come at a premium especially for SMEs trying to automate. Buyers are demanding lower cost, higher value, and quicker ROI.
Supply Chain Vulnerability
Global disruptions, raw material shortages (steel, aluminum, rare-earth magnets), and logistics delays have made sourcing critical components a major obstacle.
Aggressive Low-Cost Competition
Manufacturers in emerging markets are undercutting prices sometimes at the cost of reliability, but enough to disrupt global price points.
Conclusion
The evolution of the linear motion industry is no longer a trend, it’s a transformation. New technologies like AI-powered actuators, cobot-ready systems, and real-time motion analytics are changing the rules of performance. Forward-thinking businesses are no longer just buying components; they’re investing in intelligent motion ecosystems. If you want to stay ahead, don’t just keep up leap forward with motion solutions designed for what’s next.

